HDMI Pinout Simplified: What You Need to Know Now
High Definition Multimedia Interface, commonly referred to as HDMI, is arguably the most common communication methods used worldwide for audio and video transmission Usually when you connect your television, computer, game console, or perhaps your home theater is connected to HDMI is inevitable half way. But, have you ever paused to think about what goes on beneath the surface of your wonderful hobby?
Understanding the magic HDMI pinout – the unsung hero of your seamless audio-visual transmission — does — can give you a lot of insight into how your devices interact
What is HDMI Pinout?
By definition, an HDMI pinout refers to the association of each pin (from the standard 19-pin configuration) of an HDMI connector to a specific function that facilitates the smooth transmission of audio and visual signals between your devices and you have received.
Understanding the HDMI pinout should not be an everyday requirement for the average consumer. However, understanding its basics can be useful, especially when solving problems or navigating the complexities of the engineering world. With this knowledge, the laptop communicates with the TV but common occurrences such as failure to transmit audio become less of a shock and a more manageable environment with tangible technological features
Understanding an HDMI pinout doesn’t have to be a confusing process, especially with a simplified guide aimed at helping you understand the basics. Let’s kick back as we embark on this enlightening journey highlighting channels in the ubiquitous HDMI cable.
Standard HDMI Pinout: Configuration & Specification
At the heart of our digital entertainment experience, orchestrating secure and accurate audio and video signals, lies the organized and polished HDMI pinouts This is a key component ensuring flawless connection to electronics between your favorite devices.
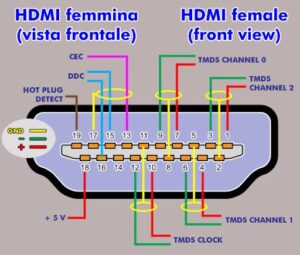
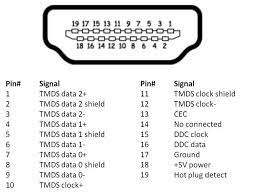
Displaying a standard 19-pin HDMI system
Standard HDMI connectors accept a 19-pin configuration. They are most likely to encounter HDMI connectors, labeled Type A, which are commonly found in televisions, gaming consoles, projectors, computers and most AV devices
Allow yourself to visualize this 19-pin system as two lines. The highest section has nine pins and the bottom row has ten pins.
Pin by Pin: Functions and Functions
Each of these pins is assigned a specific function in your HDMI system. Let’s delve into their specific responsibilities:
- Pin 1 to pin 3: These carry the TMDS data2 channel which carries video and audio data.
- Pin 4: This acts as a TMDS data2 shield, providing insulation for the data2 path.
- Pin 5 to pin 7: The Data1 path is driven by these pins, mainly for video data processing.
- Pin 8: This pin is the TMDS data1 shield, which protects the data1 channel.
- Pins 9 to pin 11: They control the data0 channel, which includes video data and less important audio data.
- Pin 12: Acts as a TMDS data0 shield, this pin provides insulation for the data0 path.
- Pin 13 & Pin 14: These pins are the keys for monitoring the data channels, sending the clock signal and at Pin 15 is protected by the clock shield.
- Pin 16: Operates in support of Device Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (DEEPROM) and is also known as DDC/CEC/HEC/HARC ground
- Pin 17: This pin provides the Hot Plug Detect function, essentially alerting the source device when the display device is connected.
- Pin 18: Reserved for future use This pin is the utility player waiting for the use.
- Pin 19: This pin provides the main voltage for the HDMI interface.
Understanding the specific role and function of each HDMI pin reveals why an HDMI connection provides such a superior audio and video experience. As technology continues to evolve, it’s not only about becoming a user but about understanding the underlying processes that shape our everyday experiences.
Various types of HDMI connections
Broadly speaking, HDMI connections are your bridge between devices, enabling high-quality audio and video data transfers. However, not all bridges are equal. A variety of HDMI connectors cater to the various sizes, functions and specifications of devices in the tech universe.
HDMI connections: A fast
There are five main types of HDMI connections you may encounter in various tech environments. Here is an overview of each.
- Type A (Standard HDMI Connector): This is the most common type, found in most major consumer devices such as TVs, gaming consoles, and home computers It uses a standard 19-pin configuration.
- Type B (Dual-Link HDMI Connector): This type has a large 29-pin configuration designed to handle very high-end displays, commonly used commercially but its use has been limited by bandwidth higher power for such resolutions Type A is treated normally .
- Type C (Mini HDMI Connector): This is a scaled-down version of Type A, retaining the 19-pin design but with a smaller form factor. Type C is therefore commonly found in smaller devices such as tablets and DSLR cameras.
- Type D (Micro HDMI Connector): This is even smaller than Type C, again the same 19-pin design but much smaller. It is designed for more compact devices such as smartphones and action cameras.
- Type E (Automotive HDMI Connector): Specifically designed for automotive applications, it features a 19-pin design with a locking mechanism to provide connectivity in the high vibration conditions typical of passenger vehicles .
Pinout Differences Among HDMI Connectors
While all types of connectors uphold the standard 19-pin layout (with the exception of Type B), the variations are more about form and compatibility rather than function. Each pin in Types A, C, D, and E corresponds to the same role, differing primarily in their physical design and compatibility with diverse devices. Type B stands as an outlier with ten additional pins devoted to increased bandwidth for higher resolution displays, yet its adoption has remained limited.
When considering HDMI pinouts, the crucial part is understanding the standard setup. From there, regardless of the type of HDMI connector in your hand, the underlying function largely remains the same. The evolving variations are the industry’s response to the ever-changing landscape of device designs and their specific needs.
HDMI vs. Other Connectors
While HDMI connectors are the frequently embraced heroes of modern digital video and audio transmission, they’re not the sole players in the game. Other connectors like DVI, VGA, and DisplayPort play their roles. Let’s compare these diverse pinout systems and learn why HDMI often takes the center stage.
HDMI and DVI compatible
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) and HDMI share the same family of TMDS (Transition-Minimized Differential Signaling) technology. Therefore, those pinouts exhibit a high level of similarity for video signals. The main difference, however, lies in the way audio and physical communication is used:
- Audio transmission: Unlike HDMI, DVI does not support audio transmission. This often requires additional cables for sound when using DVI, which slows down the smoothness somewhat.
- Appearance: Compared to HDMI, DVI connections are bulkier and less user-friendly.
between HDMI and VGA
VGA (Video Graphics Array) is an older video standard that relies on analog signals. VGA and HDMI have opposite pinout paths, resulting in very distinct display profiles:
- Signal quality: Because HDMI uses a digital signal, it offers better video and audio quality compared to VGA, making HDMI the go-to for today’s premium devices.
- Audio transmission: VGA transmits only video signals, requiring a separate audio cable, unlike HDMI, which handles both with a single cable.
HDMI and DisplayPort
Like HDMI, DisplayPort is a modern digital interface. Although their pinouts support similar functions, they have different preferred applications:
- Display: Provides high-quality digital video and audio from both HDMI and DisplayPort. DisplayPort can handle large bandwidths, especially benefiting from high-resolution displays and multiple daisy-chaining monitors.
- Device compatibility: HDMI features prominently on consumer devices. DisplayPort is commonly found in high-end monitors and professional grade graphics cards.
Why HDMI is often preferred
The HDMI connection plays a huge role in our audio and video experiences for a few important reasons:
- All-inclusive transmission: HDMI’s 19-pin design allows it to transmit both audio and video signals simultaneously, a step up from DVI and VGA, which only handle video.
- Universal compatibility: HDMI connectors are widely used in many devices from flagship TVs to gaming console laptops, assuring compatibility with a wide range of applications
- Easy-to-use design: Due to its compact size and ease of use, HDMI offers a hassle-free interface, unlike larger DVIs or older VGA connections.
- High-Quality Digital Signal: By delivering clean, uncompressed digital signals, HDMI guarantees an excellent quality audio-visual experience.
In the battle of connectors, the versatile and user-friendly HDMI often emerges as the preferred choice. Yet, the best connector for your requirements depends on your specific devices and usage scenarios.
Practical Application of HDMI Pinouts
Understanding HDMI pinouts can be extremely beneficial in diagnosing cable-related issues and facilitating more adept usage of your digital devices. Let’s delve into how to employ this knowledge and address some common troubles.
Using HDMI Cables Based On Pinout
A practical grasp of HDMI pinout can help you make informed choices while connecting your devices. While HDMI cables are inherently user-friendly, it’s helpful to remember:
- All-in-one Solution: Each pin on the HDMI connector plays a particular role in transmitting audio-visual data. So, one cable efficiently manages both high-definition video and audio signals.
- Unidirectional: HDMI pins enable unidirectional signal flow. There’s a source device, such as a gaming console, and a sink device, like a TV monitor. Identifying source and sink correctly ensures seamless functioning of your setup.
HDMI Pinout Troubleshooting
Even at its simplest, HDMI users are not immune to problems such as no signal or poor transmission quality. Here’s how understanding the HDMI pinout can help troubleshoot:
- Check for connected pins: A connected or broken pin can interrupt data transmission. Often, a closer look at the condition of the wires can reveal the source of the problem.
- Checking cable quality: Poor quality cables do not support HDMI’s 19-pin standard properly, causing problems with transmission. Knowing the pinout standard can guide you to high-quality cables.
Future trends in HDMI technology
As the technology evolves, HDMI also regularly introduces new versions and specifications. These changes may affect future pinout designs. Let’s take a look at what the future holds for HDMI.
HDMI pinouts future
Despite constantly improving technology, the 19-pin system for HDMI has been surprisingly durable. Here are a few trends to note.
- Higher bandwidth: As the demand for higher resolution and higher refresh rates increases, so does the need for more bandwidth. Future HDMI versions may introduce changes in pin configuration or functionality to facilitate this.
- Enhanced cable specifications: Looking ahead, we can expect a new range of HDMI cables that promise better performance without the need for pinout design changes.
conclusion
Understanding the HDMI pinout gives us a practical idea of how the HDMI cable acts as an efficient bridge between our devices. With a robust and useful 19-pin design, HDMI allows high-quality audio and video data. As technology continues to evolve, it’s important to remain aware of potential changes to HDMI specifications and pin settings, to help enhance your AV experiences.
Remember that HDMI—along with its pinouts—is about convenience, efficiency, and quality. Knowing the role of each pin gives you insight into how to troubleshoot efficiently and tap into the full potential of an HDMI connection.